
Pathol 4:401.īertheussen, K., 1979, The cytotoxic reaction in allogeneic mixtures of echinoid phagocytes, Exp.

B., and Lemma, A., 1962, Bacterial infection and reaction to injury in some echinoderms, J. This process is experimental and the keywords may be updated as the learning algorithm improves.īang, F. These keywords were added by machine and not by the authors.
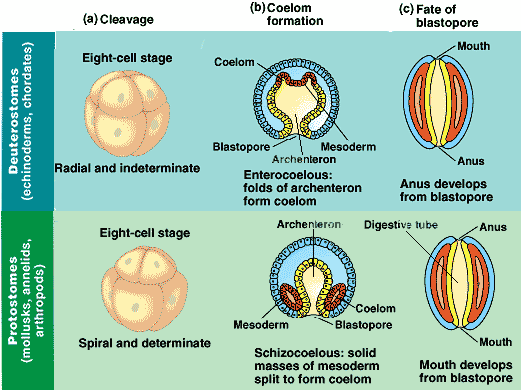
During later development, the two groups also differ in formation of mesoderm and the coelomic cavity. Cleavage is said to be determinate in the latter case. It does not occur in protostomes, where removal of blastomeres results in deformed embryos. Early separation of the blastomeres in deuterostomes gives rise to complete individuals this type of development is known as indeterminate cleavage. Cells are oriented in a spiral pattern in protostomes, whereas the blastomeres are positioned directly upon one another in the deuterostomes, resulting in a radial cleavage pattern. The pattern of cell cleavage also varies in the two groups. The blastopore gives rise to the anus in deuterostomes (“mouth later”), while the mouth develops as a separate invagination. “Protostome” is Greek for “mouth first” and in this group, the mouth is derived from the embryonic blastopore. The two groups are distinguished on the basis of major differences in early development, which may suggest that they were derived from different ancestors. Both the echinoderms and the vertebrates are deuterostomes, while all other invertebrates are classified as protostomes.

During the early Precambrian period, the animal kingdom is believed to have diverged into two major groups, known as the deuterostomes and the protostomes. The echinoderms are of particular interest in phylogenetic studies because of their relatedness to the vertebrate subphylum.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
